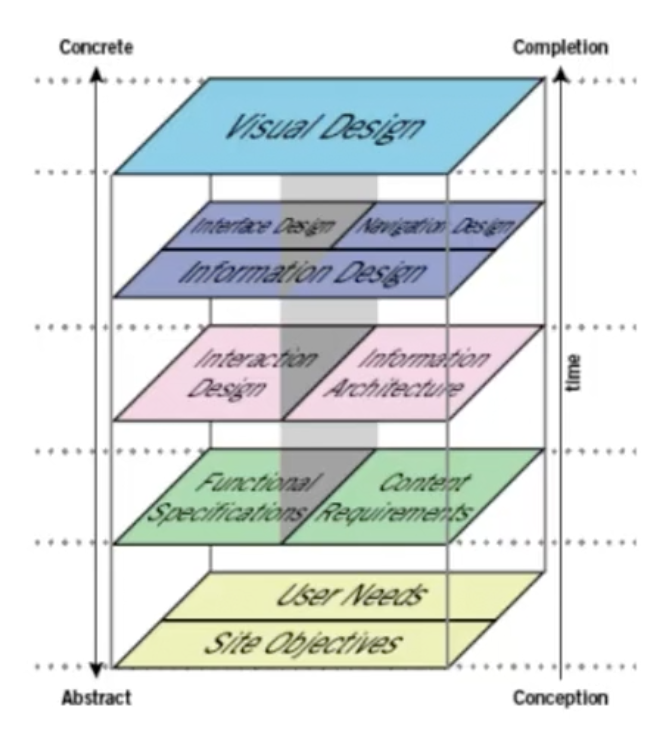
Reflection
The user interface works closely with user experience to join together to create a more well-rounded and sophisticated website and user experience. The term is used to explain how the user and a computer system interact.
There are 4 main navigation patterns and they are
Tabs: Navigation and module tabs. Tabs help separate information into sections and is accessible in a navigation system.
Menus: Horizontal dropdown, vertical dropdown, vertical dropdown. Used to help user navigate through sections. Useful when there is limited space on the page, creates less clutter.
Content: Carousel, Event Calendar, Article list. These are used to save space on a page and to lessen clutter.
Jumping in hierarchy: Shortcut dropdown, Fat footer, Home link and Breadcrumbs