Every Last Drop
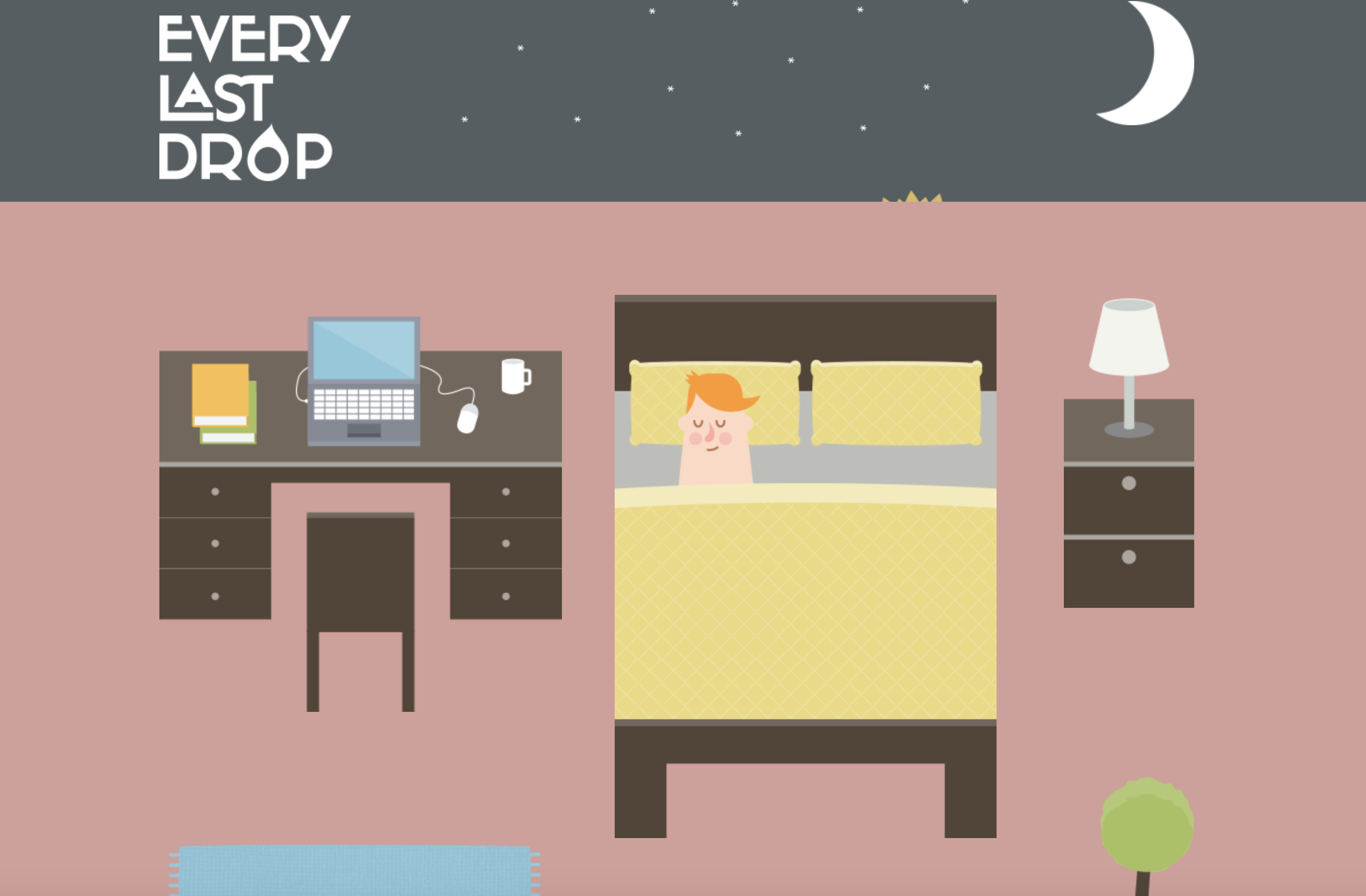



What is the interactive about?
– This interactive website informs people about how much water is wasted daily
– Includes ways to reduce the amount of waste being made
– Provides short yet informative points (gets straight to the point)
– Places emphasis on why “every last drop” counts
– Informs that water isn’t just wasted on showers or washing the dishes, but is also wasted in other areas in our lifestyle – water is wasted depending what brand of clothes you buy or even the type of food you eat.
Who is it designed for? (Target Audience)
– The website is designed for any age as the text is only of a few words and the interactive animation visually helps the audience to understand the fundamental points of water waste.
– particularly useful for a younger audience as the colours and simple illustrations help convey the meaning in a clear and interesting way. Though it’s combination of illustration and factual text makes it a useful website for all
What knowledge does it assume of the target audience i.e. digital literacy?
- They assume the audience is able to read
- Have access to a computer and be able to correctly use it
- The knowledge of what an average morning routine looks like
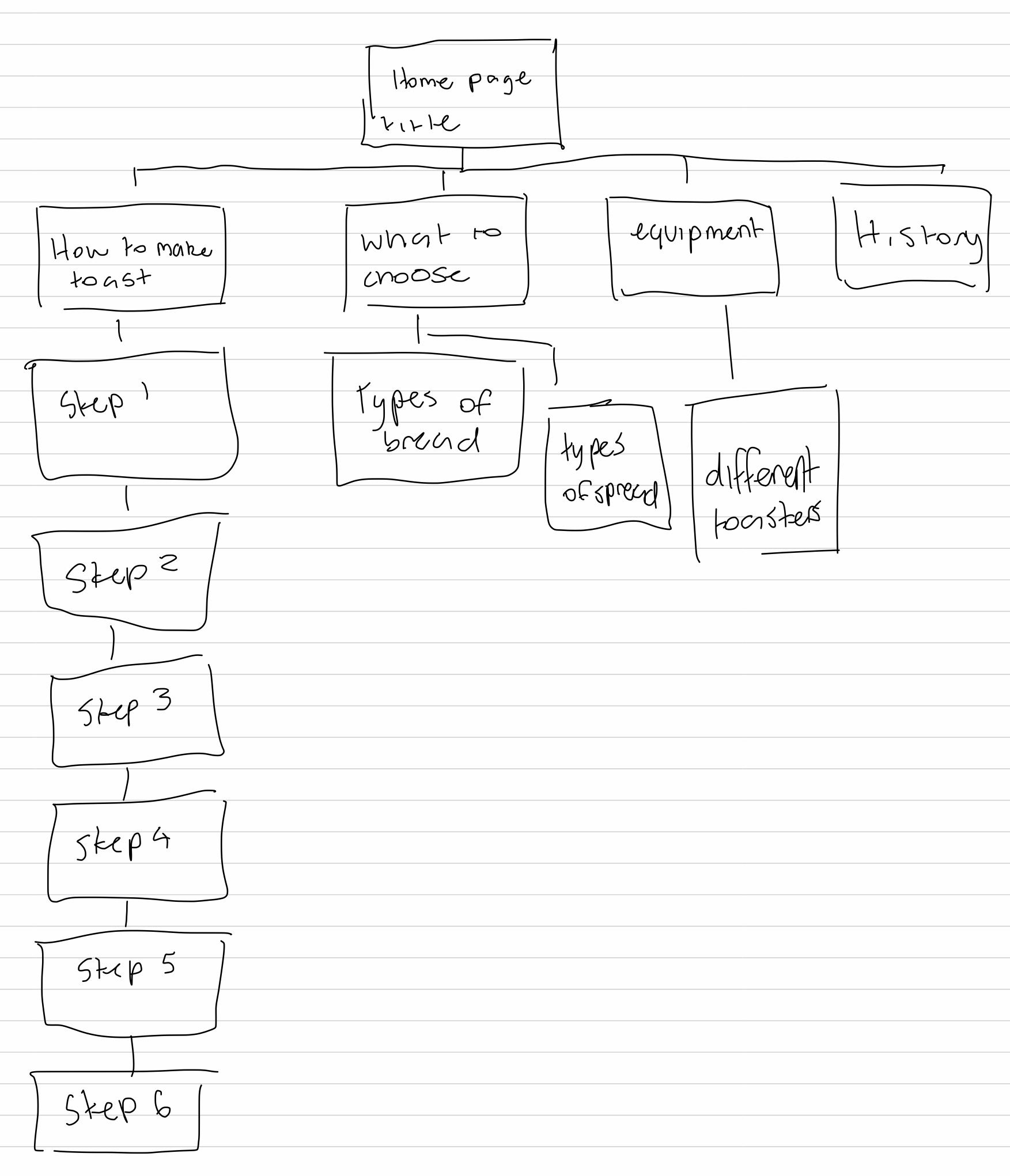
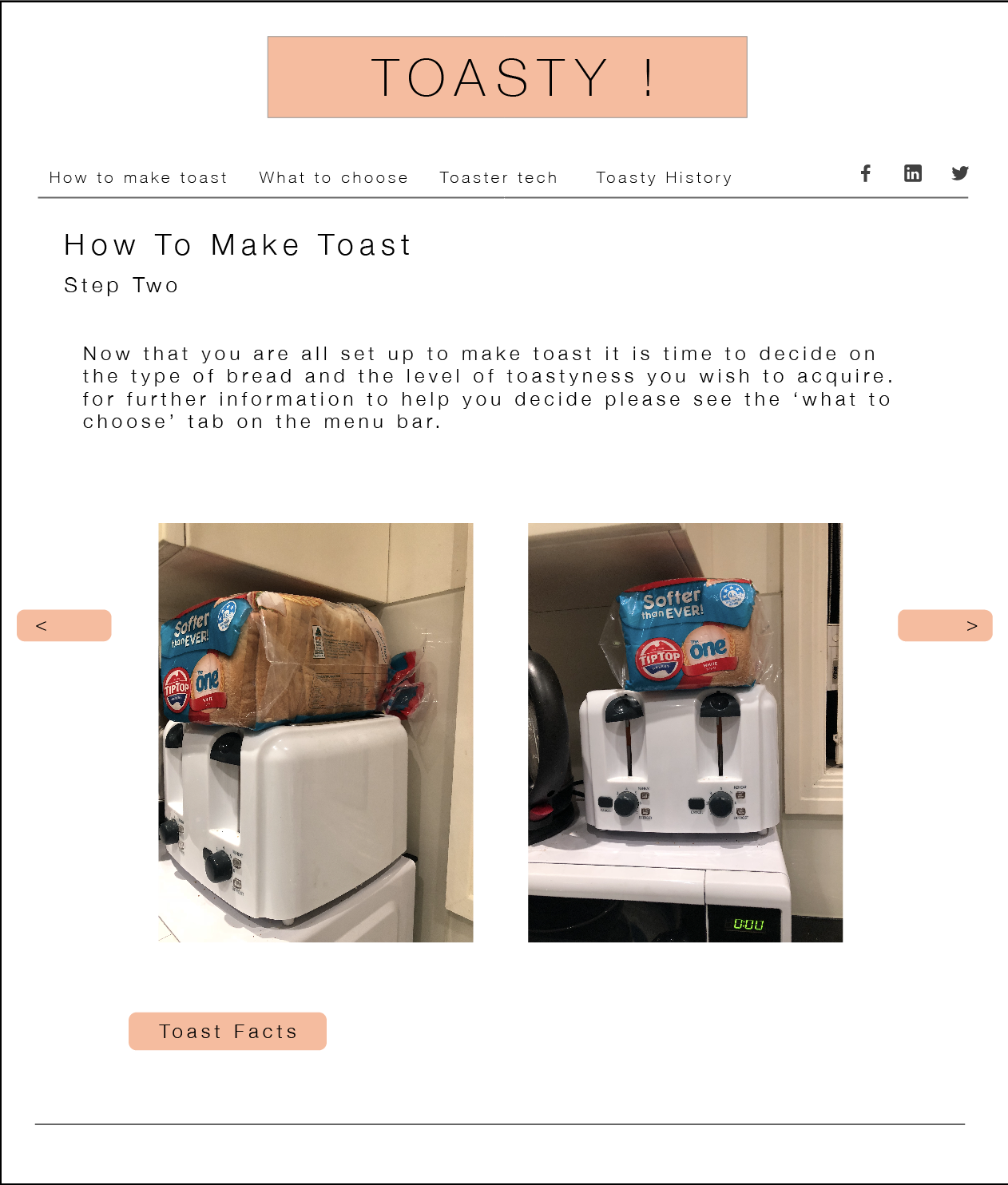
Describe the type of user interactions, and the user interface.
– User must scroll down the page to see the sequence of information being portrayed
– Each time the user scrolls down the page animations from a scene disperse and then form together to create the next scene
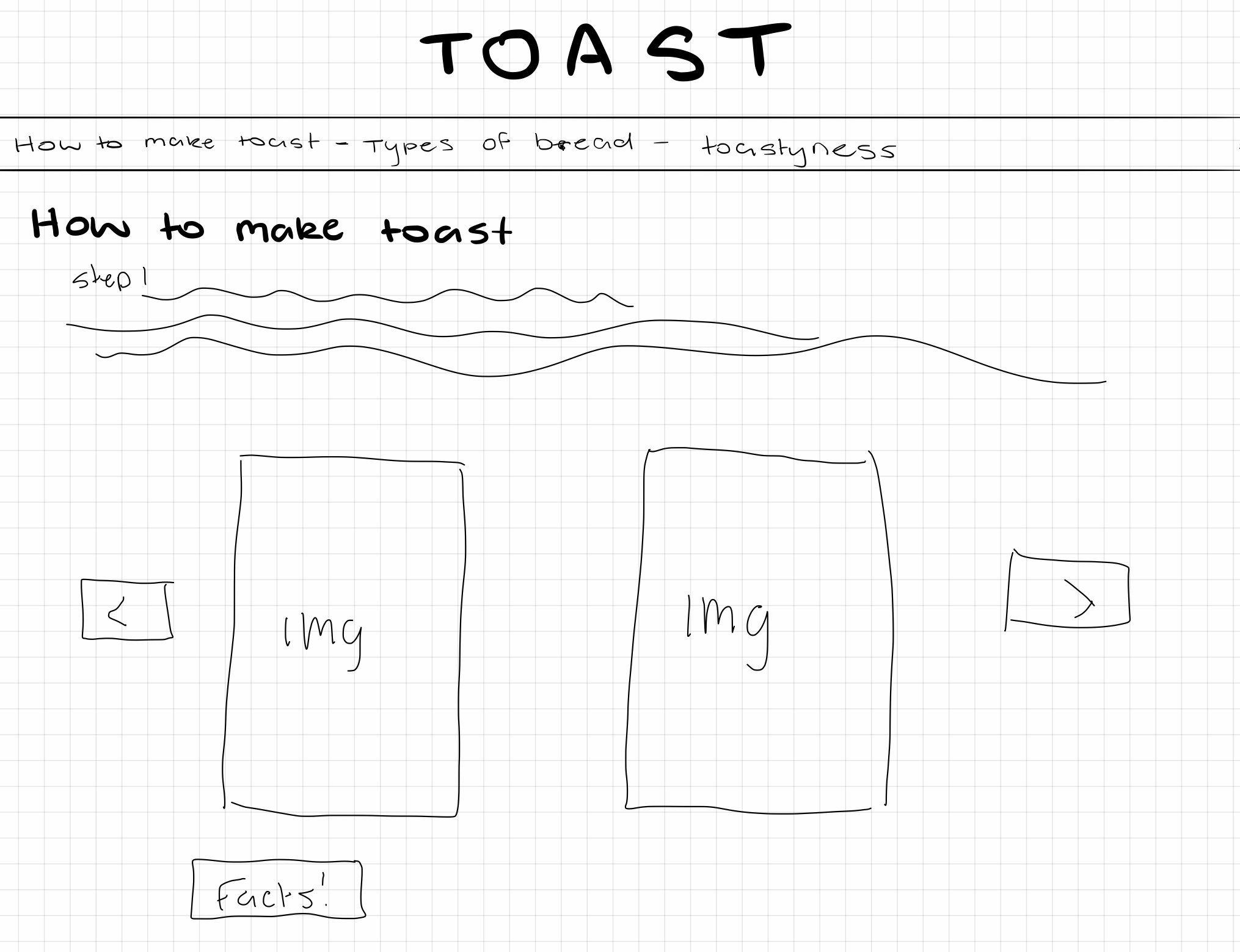
What can you say about the visual design – layout, colour, and typography? How would you describe the style?
– The style of this website is heavily made in an illustrative style, or cartoon like animation as the objects created are very simple
– The layout is user friendly on all devices. The layout is also very simple as the user only interacts with the website by scrolling
– The colours are vibrant and fun, making it interesting to look at and appealing to the eye.
– The typography is simple and easy to read. The typography changes with each scene to suit the environment
What improvements would you suggest?
– A clearer understanding of how to navigate through this website, i.e. a more striking and noticeable arrow or sign directing the user to scroll down.
– Improvement would be having an introduction or brief story into what the user is about to be reading
– The facts could be expanded and more information about how and why so much water is lost
– Provide the user with a deeper understanding as to why it is so beneficial. I.e what are the long term impacts of wasting so much water?
– more specific information could be added to teach the audience how to lower their water usage